Enamel hypoplasia sure sounds like something to be afraid of, doesn’t it? But there’s no need to panic just yet. We’re here to clear up any misunderstandings and reassure you that this is a treatable issue.
Enamel hypoplasia refers to dental enamel that is inadequate or undeveloped. But first, let’s define enamel. It’s the tough, protective layer surrounding your teeth on the outside.
Your enamel, which is largely mineral-based compounds that your body manufactures to construct your teeth, is the “white component” of your teeth.
When enamel is growing in the mouth, many circumstances might induce a “glitch” in the process, resulting in regions of the enamel that are weaker than they should be.
This can appear as lines across the surface of one or more teeth, or it can appear as a discoloration on the teeth. In rare circumstances, a dark brown discoloration might cover the entire tooth.
What Are the Signs of Enamel Hypoplasia?
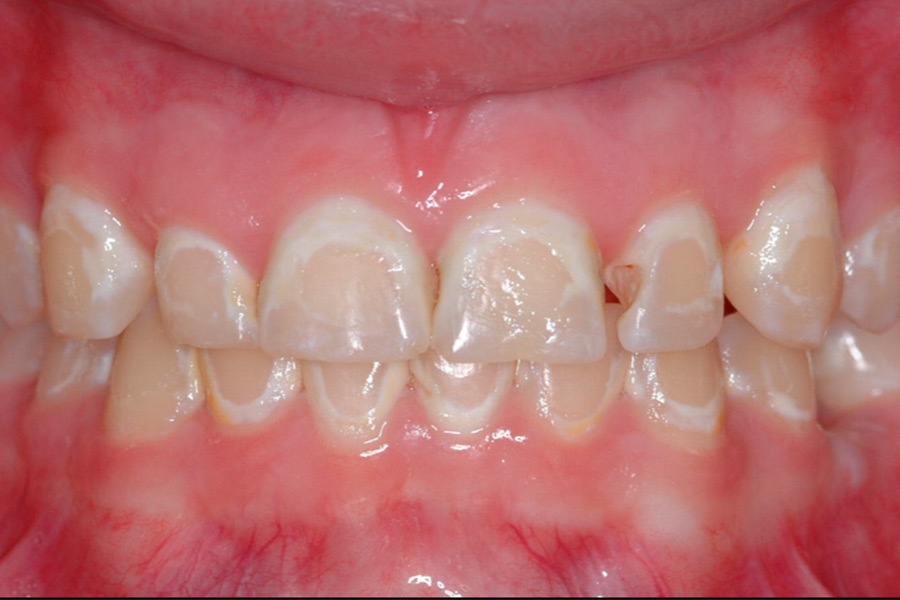
Some indicators of enamel hypoplasia are clear, while others are more difficult to spot and may go unnoticed until they cause serious dental issues. Excessively thin tooth enamel can cause:
- Pits, groves, depressions, and fissures
- White spots
- Stains that are yellowish-brown in color (where the underlying layer of dentin is exposed)
- Heat and cold sensitivity
- Tooth contact is missing, and teeth are wearing unevenly
- Acid sensitivity to foods and beverages
- Germs that are dangerous to humans
- Tooth decay and cavities are more likely to occur
Enamel Hypoplasia Causes
When the unique cells that generate tooth enamel are disrupted during a specific stage of enamel creation, enamel hypoplasia ensues. A wide range of causes, including hereditary and environmental influences, can potentially produce such a disruption.
Enamel hypoplasia in children comes from a variety of hereditary factors, the majority of which are relatively uncommon genetic illnesses, such as:
- Usher syndrome
- Seckel syndrome
- Ellis-van Creveld syndrome
- Treacher Collins syndrome
- Otodental syndrome
- 22q11 deletion syndrome (velocardiofacial syndrome)
- Heimler syndrome
Enamel hypoplasia is the result of a number of reasons, including the following:
- Traumatic dental injury
- Infection
- A lack of calcium
- Vitamin A, C, and D deficiency
- Liver illness, jaundice
- Celiac disease is a type of celiac disease
- Cerebral palsy by an infection in the mother or fetus
Enamel Hypoplasia Treatment
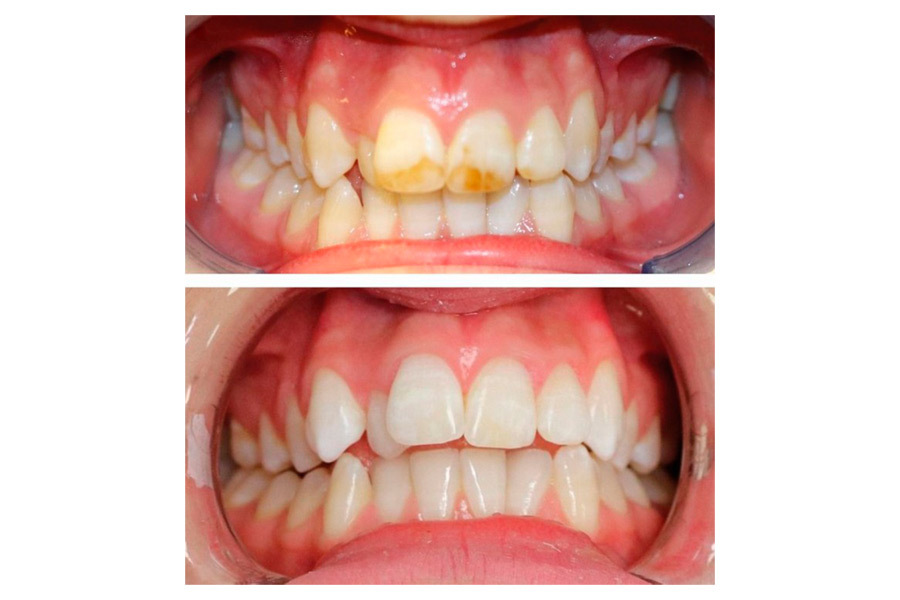
The severity of the problem will determine which treatment for enamel hypoplasia you’ll nee1d. Dentists may recommend routine maintenance and care in milder cases, with specific attention to the affected area to avoid tooth decay. Some circumstances may necessitate cosmetic changes.
The importance of early detection and diagnosis cannot be overstated. That is why youngsters should consult a dentist between the advent of their first tooth and their first birthday. The treatment’s objectives are to:
- tooth decay prevention
- keep a healthy bite
- keep the structure of your teeth
- keep your teeth in good shape
Smaller flaws that aren’t causing deterioration or sensitivity may not require immediate correction. They do, however, need to be watched. To help safeguard teeth, your dentist will most likely use topical fluoride.
Treatment options for sensitivity, cavities, or tooth structure exhibiting wear include:
- Enamel microabrasion: This treatment uses acids and abrasive materials such as hydrochloric acid and silicon carbide to eliminate stains and discoloration on the enamel. The surface of your teeth may then be coated with a composite resin by your dentist.
- Resin infiltration: This is a non-invasive procedure for reducing the appearance of white spots. It entails putting a resin directly on your teeth’ white areas. Because the resin reflects light in the same manner that your teeth do, it’s simple to match the natural appearance of your teeth.
- Crowns: they protect the tooth from infection and bacteria by covering it.
- Enamel microabrasion is a minimally invasive process that improves the appearance of the teeth by making them whiter and healthier.
- Professional teeth whitening: This effectively makes the contrast between the white spots and the rest of your teeth less noticeable. After preparing your teeth, your dentist will apply a bleaching gel for roughly 40 minutes. However, this may not be enough if you have deeper white patches.
Overall, home care is essential. To keep EH and hypomineralization under control later, children must practice good oral hygiene now.
However, the best thing you can do is talk to your dentist about getting the correct treatment as soon as possible so that you or your child may work toward having the healthiest, brightest smile possible.c
All of our patients, especially those with hypoplastic teeth, should practice good dental hygiene and eat a nutritious diet. Brushing twice a day with fluoridated toothpaste will be beneficial for your teeth.
Maintain a low-sugar diet and try to stay away from sticky foods! Remember to see your dentist for an examination, professional cleaning, and fluoride application at least twice a year.
Visit Trust Dental Care to have the best experts take care of your smile while saving time and money in the process. Contact us today!




Leave a Reply